|
|
|
|
|
AN ANALYTICAL ASSESSMENT OF HOW ACCOUNTING APPLICATIONS ENHANCE THE EFFICIENCY OF FINANCIAL RECORD MANAGEMENT
Ananya Patel 1![]() ,
Amol Jayprakash Bhalerao 2, Dr. Bhawna
Sharma
,
Amol Jayprakash Bhalerao 2, Dr. Bhawna
Sharma
1 BBA
3rd Year (Hons), Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Mumbai, India
2 Assistant
Professor, Amity Business School, Amity University Mumbai, Mumbai, India
3 Director International
Affairs and Programs, Officiating HOI, Amity Business School, Amity University
Mumbai, Mumbai, India
|
|
ABSTRACT |
||
|
The technology evolution has brought about a complete change in the accounting profession. The financial record management has been moved from manual processes to digital automated systems. This paper presents a thorough analytical evaluation of the role of accounting applications in increasing the efficiency, dependability, and precision of the financial record management in the current organizations. The study analyzes the operation of widely accepted tools such as Tally Prime, QuickBooks, and SAP to examine the different ways such systems are able to organize data better, eliminate human error, and to some extent, decision-making is faster. The research follows a descriptive, observational, and qualitative approach, employing direct observations, secondary data, and a comparative analysis of manual and computerized systems. The study
results reveal that uses of accounting applications hasten the overall
process of daily chores drastically, ensure compliance with tax laws, elevate
the quality of reports, and at the same time, offer real-time finance
information. The accuracy of record keeping, the readiness for audit, and
overall productivity upswing reveal the remarkable power that digital systems
have over accounting workflows. Nevertheless, inescapable issues, including
user training, security of data, and maintenance of the system, still exist.
However, the net impact of using accounting software is to say the least,
very encouraging. The paper argues that contemporary firms that aspire to
keep up with efficiency, transparency, and professional standards in
financial record management can no longer rely on old manual methods. |
|||
|
Received 25 March 2025 Accepted 09 April 2025 Published 30 June 2025 DOI 10.29121/ShodhPrabandhan.v2.i1.2025.42 Funding: This research
received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial,
or not-for-profit sectors. Copyright: © 2025 The
Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 International License. With the
license CC-BY, authors retain the copyright, allowing anyone to download,
reuse, re-print, modify, distribute, and/or copy their contribution. The work
must be properly attributed to its author.
|
|||
|
Keywords: Accounting Applications, Financial Record
Management, Tally Prime, Digital Accounting, Automation, Accuracy, GST
Compliance, Financial Reporting, Bookkeeping Efficiency, Computerized
Accounting Systems |
|||
1. INTRODUCTION
The function of accounting has always been central to the administration of any organization since it guarantees that the financial transactions will be accurately recorded, classified, and reported. The traditional system of doing things consumed a lot of time and mainly depended on manual bookkeeping, physical registers, and calculators. Although it was effective in the past, the manual system has gradually become a significant source of delays, human mistakes, and difficulties in retrieving past data. Over time businesses grew, and the tax laws became complicated; hence the drawbacks of manual accounting began to be even more noticeable.
The introduction of digital accounting applications was a significant milestone in the accounting profession. The likes of Tally Prime, QuickBooks, SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Zoho Books have brought automation directly to the heart of finance management. These tools perform operations like automated ledger posting, GST calculations, bank reconciliations, inventory tracking, and real-time reporting. Processes requiring hours of manual effort can now be completed in minutes.
Financial data in huge amounts, are generated by organizations every day. If not for the digital systems, the whole process of data management would be extremely difficult, especially in compliance, audits, and monthly closing of accounts. Accounting software not only makes these processes easier but also gives a higher level of accountability and keeps the financial statements consistent. The objective of this study is to evaluate the extent to which these applications support the efficiency, professionalism, and even the necessity of their adoption in the current business settings for the management of financial records.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
The changeover from manual to computerized accounting has been thoroughly researched and reported by various scholars and accounting institutions. The digital systems are credited with their contribution to accuracy, regulatory compliance, and overall company productivity in numerous research studies.
According to Gupta and Mehra (2023), the movement from physical ledgers to cloud-enabled accounting has cut down the burden of accountants to a great extent. They point out that electronic applications lower the chances of errors in calculations, and the resulting documents are quick to obtain and verify. In a like manner, Sharma and Jain (2022) contend that automation allows accountants to shift their focus from the tedious job of posting and reconciliation to that of being an analyst and giving advice.
Rani (2021) cites that one of the main benefits of accounting apps is the accuracy of the financial statements that gets better. Manual calculation is often a source of posting errors, erroneous ledger balances, and discrepancies in reports; on the contrary, computerized systems abide by stringent guidelines, perform automatic checks, and keep uniform financial records. Tally Solutions (2024) claims that its Tally Prime software encompasses various functionalities such as GST automation, inventory management, multi-ledger posting, and one-click generation of financial reports. To elaborate on that, Singh (2023) indicates that the software has gained popularity owing to its affordability, ease of use, and trustworthiness, mainly among small and medium-sized businesses.
Nonetheless, there are hurdles that need to be overcome. According to the findings of Kaur and Bansal (2021), one of the biggest contributors to this problem is the lack of trust that employees have in the digital tools. The process of educating the workforce demands both time and money. The concern for data protection and security along with other issues has been highlighted by OECD (2023) as the primary obstacles that companies face during the process of moving to cloud-based accounting systems. Generally speaking, the literature supports that the use of accounting applications brings about a tremendous increase in productivity; however, it also means that the organizations will have to provide training and invest in data security measures systematically.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The current study applies a methodological framework that is both descriptive and qualitative for the purpose of examining the role that accounting applications play in enhancing the efficiency of financial record management. The method calls for the observation of accounting processes in practice and the evaluation of tasks carried out manually vis-a-vis those performed on a computer.
3.1. Primary Data
Direct Observation: Following the steps of entering vouchers, calculating GST, posting to ledgers, and reporting finances through accounting software.
Hands-on Experience: Making entries and reports to realize the speed and precision of financial data processing through the software.
Informal Conversations: Brief talks with the accounting personnel to acquire the knowledge of actual obstacles and advantages that the use of digital tools brings.
3.2. Secondary Data
Textbooks and academic studies on computerized accounting plus that of the accounting professionals' institutes (ICAI) through guidelines and standards.
Documentation of the software, especially user manuals for Tally Prime. Literature and internet resources concerning the digital transformation in accounting.
Innovative research papers in the domain of automatic systems, compliance in GST, and financial reporting systems.
3.3. Method of Analysis
A comparative method was used.
Manual accounting tasks—such as voucher entry, GST calculation, and report preparation—were timed and compared with the same tasks performed using accounting software.
Two charts were prepared to support the analysis:
· Chart 1: Time Comparison (Manual vs Software)
· Chart 2: Error Reduction (Manual vs Software)
These charts visually show how software improves speed and accuracy.
3.4. Scope of the Study
The study focuses on:
· The impact of digital accounting applications on efficiency
· Improvements in accuracy, reporting, and compliance
· Tasks such as voucher entry, GST processing, ledger posting, and financial reporting
· General accounting environments (not only one organization)
4. ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
4.1. Time Efficiency
Accounting software completes tasks much faster than manual methods.
The Time Comparison Chart Chart 1 shows how long common accounting tasks take manually vs. using software.
Chart 1
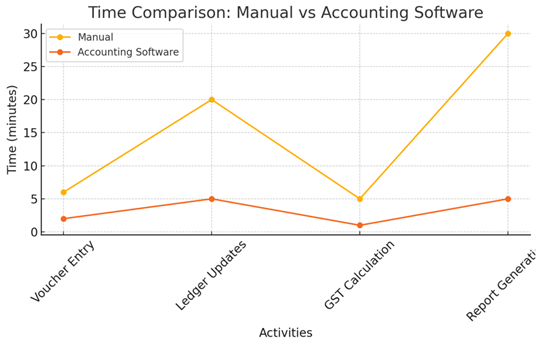
|
Chart 1 Time Comparison – Manual vs Accounting Software |
Explanation:
· Voucher Entry: It takes time to manually calculate totals and enter the details with precision. In the software, the values are filled in automatically, and the GST is calculated automatically, so the whole process is quicker.
· Ledger Updates: The process of manually updating ledgers consists of writing down the entries and ensuring that the totals match. With software, the ledgers are updated automatically every time a voucher is entered
· GST Calculations: Certainly making manual GST calculations is prone to errors and is time-consuming, whereas software automatically generates and maintains tax calculations
· Report Generation: Financial statements, which include reports like Profit and Loss, Trial Balance, and Balance Sheets, have to undergo manual checking and writing, which requires a lot of time. By utilizing the stored data, software generates these reports in just a few seconds
The graph titled “Error Reduction” Chart 2 shows that the use of digital accounting systems greatly decreases the overall error rate in financial records.
Chart 2
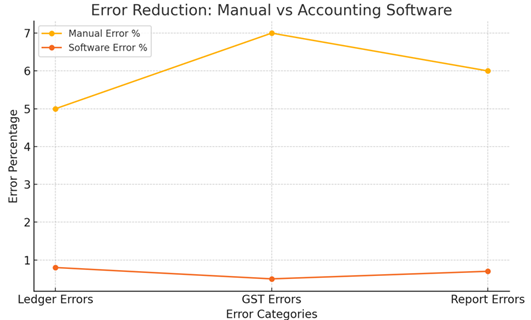
|
Chart 2 Error Reduction – Manual vs Accounting Software |
Explanation:
• Ledger Errors: Mistakes like wrong figures, missing entries, or misclassification of accounts are common in manual entries. These problems are lessened by accounting software since each voucher is posted to the right ledger automatically, thereby lessening human error due to judgment.
• GST Errors: The correct tax rate must be applied, and the classifications of CGST, SGST, and IGST distinguished while computing GST. The digital software takes over these activities, guaranteeing precision in tax calculation and avoiding errors in manual calculations.
• Report Inconsistencies: Implementing manual accounting might result in discrepancies between ledgers and reports because of unadjusted items or calculation mistakes. Whenever a voucher is posted, software immediately updates all journals and ledgers registered against it, thus, the statements will not have any differences
5. Reporting and Compliance
Accounting applications are capable of generating essential financial statements—such as the Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss Statement, Trial Balance, and GST summary—in just a few seconds.
Explanation:
• As soon as the data is inputted, the software will instantly process all the financial data and, thus, allow the generation of reports in real time.
• The reports are in standardized formats that have been approved universally by auditors, accountants, and tax authorities.
• Invoices ready for GST, reports of tax liability, and input credit summaries are the measures that guarantee full compliance with the statutory requirements.
• Automated reporting minimizes the likelihood of mistakes in tax declarations and, at the same time, significantly cuts down the time needed for audits.
6. FINDINGS
Through examination of the differences between manual accounting methods and accounting software, a few key findings were able to be distinguished:
1) Reduction
of Errors to a Great Extent
The implementation of digital accounting systems has a significant impact on the error rate, especially in recording transactions, computing GST, and preparing financial statements. The system's internal checks and immediate updating of the ledger are contributing factors that keep the errors normally associated with manual bookkeeping at bay.
2) Time
Efficiency is a Major Improvement
The use of accounting software reduces the time for activities such as entry of vouchers, GST computation, posting in the ledgers, and preparing reports to a mere fraction of the time required without it. With the use of software, accountants can devote their time and effort more on analysis and decision-making rather than on repetitive clerical tasks.
3) Reporting
Accuracy Has Been Improved
The financial statements produced by the software are accurate, uniform, and readily accessible. The processing of data in real-time eliminates the waiting time and guarantees that the management is using the most current financial data.
4) Strong
Compliance Support
The tax invoices, tax summaries, and statutory reports produced by the software make sure that the company complies with the regulations set by the government. Automation is a tool that not just lessens the filing errors but also minimizes the likelihood of penalties due to incorrect tax reporting.
5) Data
Organization and Accessibility Has Improved
With digital records, the structure is better, and it is easier to retrieve them and the searching can be done in a highly effective way. This is one of the main factors leading to better audit trails, greater transparency, and reduced risk of data loss that is usually associated with manual record-keeping.
6) Decision-Making
Has Improved
The management can be more accurate in their financial performance evaluation and therefore make really good decisions in areas of cost, budget, cash flow, and planning through the use of real-time reports.
7. CONCLUSION
The research has made the assertion that accounting software applications are very crucial in the process of managing financial records through their efficiency, accuracy, and reliability improvements. Digital tools are replacing the traditional tedious manual works with the automated process of faster, more consistent and less error prone.
Above all, accounting software delivers superior financial management and guaranteed compliance with the law via real-time reports and automatic GST compliance. The data is more organized, clear, and available for everyone hence the audits and internal reviews are less complicated.
Organizations may have to deal with difficulties such as those of training their staff, updating systems, or securing data but still, the computerized accounting systems have benefits that greatly surpass these drawbacks. In the current digitized world, accounting applications have become indispensable in the fields of maintaining professionalism, lowering workloads, and producing better financial information for decision-making.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
None.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
REFERENCES
Gupta, A., and Mehra, R. (2023). Computerized Accounting and Information Systems. McGraw Hill.
Institute of Chartered
Accountants of India (ICAI). (2024). Guidance Note
on Computer-Based Accounting Systems. ICAI Publications.
Kaur, S., and Bansal, P. (2021). Challenges in Implementing Accounting Software in Indian Firms.
International Journal of Accounting Research, 9(2), 33–41.
Organisation for Economic
Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2023).
Digital Transformation in Accounting Practices. OECD Publishing.
Patel, R. (2022). Effectiveness of Computerized Accounting In Improving Financial
Reporting Accuracy. International Journal Of Finance And Technology, 6(1),
55–63.
Rani, S. (2021). Digital Accounting and Accuracy Improvement. Journal of Finance and
Auditing, 9(1), 28–35.
Sharma, R., and Jain, P. (2022). Role of Automation in Financial Accounting. Indian Journal of
Accounting, 12(4), 45–52.
Singh, K. (2023). Impact of Digital Tools on Accounting Firms. Business Review Journal,
15(3), 18–25.
|
|
 This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
© ShodhPrabandhan 2025. All Rights Reserved.